In a world that is becoming more concerned with sustainable living and the preservation of resources, aquaponics has emerged as a ray of light offering promise for farming that is self-sufficient. This cutting-edge method of farming combines aquaculture and hydroponics in a way that is complementary to one another, resulting in the creation of a self-sustaining ecosystem in which the existence of both plants and fish is beneficial.
This comprehensive guide dives into the fundamentals of aquaponics, which is a farming method that is kind to the environment. This article will provide you with invaluable insights and helpful advice to assist you in beginning your journey into aquaponics. Whether you are a city dweller with limited space or a rural homesteader seeking an efficient way to grow fresh produce and raise fish, this article will be of great assistance to you.
This guide will take you step-by-step through the fundamentals of aquaponics, from gaining an understanding of the delicate equilibrium that exists between fish and plants to the process of designing and maintaining an independent system. You will gain the knowledge and confidence to set up your off-grid aquaponic farm in your backyard by following the clear explanations, illustrative diagrams, and step-by-step instructions provided in this book. This farm will produce wholesome, organic food right in your backyard.
Join us as we explore methods of farming that have a minimal impact on the environment and find out how aquaponics has the potential to transform the way we cultivate and eat our food, thereby providing a road map for a more sustainable and environmentally conscious future.
The Importance of Sustainable Farming
A more environmentally conscious and resilient future will be built on the foundation of sustainable farming practices. The ever-increasing needs of the world’s population in terms of both food and resources are exerting a massive amount of pressure on the planet’s ecosystems. Conventional agriculture, which is frequently dependent on large amounts of chemical inputs and large-scale monoculture, is a contributor to the degradation of soil, the pollution of water, and the emission of greenhouse gases. Sustainable farming practices give priority to regenerative methods that reduce the amount of damage done to the environment while simultaneously producing food that is high in nutrients and is sourced locally. It’s an important stepping stone on the path to a more harmonious relationship between people and the natural world.
What is Aquaponics?
Aquaponics is a model of sustainable agriculture that successfully integrates aquaculture and hydroponics into a single productive ecosystem. Fish and plants can coexist in harmony thanks to this ingenious system, which provides advantages to both parties. Within the confines of this closed-loop ecosystem, fish waste serves as a source of vital nutrients for plants, while the plants, in turn, filter and clean the water that the fish swim in. This sophisticated cycle does not require the use of soil, pesticides, or an excessive amount of water; as a result, it is an exceptionally effective and resource-friendly method for cultivating both fish and crops. It is both a demonstration of the power of sustainable innovation and a testament to the intricate balance that nature maintains.
Why Aquaponics for Off-Grid Living?
Self-Sufficiency in Limited Spaces
One of the most significant benefits of aquaponics, particularly when it comes to living off the grid, is the system’s adaptability to living in confined spaces. This method of compact farming can be successful in both urban and remote settings, particularly those with a limited amount of arable land. Aquaponics gives individuals and communities the ability to grow their food even in the smallest of spaces by utilizing vertical growing systems and compact fish tanks.
Reduced Dependency on External Resources
Living off the grid frequently involves the pursuit of greater levels of self-sufficiency. Aquaponics is an excellent method for achieving this objective because it reduces reliance on outside resources. In many cases, conventional farming calls for an ongoing supply of water, fertilizers, and pesticides to be applied to the land. In an aquaponic system, the water is reused, and the fish and plants collaborate to produce an ecosystem that can maintain itself. This type of system is known as self-sustaining. This provides a level of independence that is necessary for off-grid living and significantly reduces the amount of reliance that is required on inputs from the outside world.
Energy Efficiency
Living off the grid necessitates a frugal approach to the management of resources, particularly energy. When compared to more traditional methods of farming, aquaponic systems have a significantly lower energy footprint. They only require a small amount of electricity to power pumps and keep water circulating, particularly when they are designed with energy-saving features in mind. Because of this, aquaponics is a fantastic option for those who want to reduce their impact on the surrounding environment while simultaneously living off the grid.
Components of an Aquaponics System
Fish Tank
The fish tank is the heart of any successful aquaponics system. Fish, most commonly species such as tilapia, catfish, or trout, can flourish and produce waste in this environment. When calculating the overall productivity of the system, the dimensions of the tank and the amount of liquid it can hold are both extremely important factors.
Grow Bed
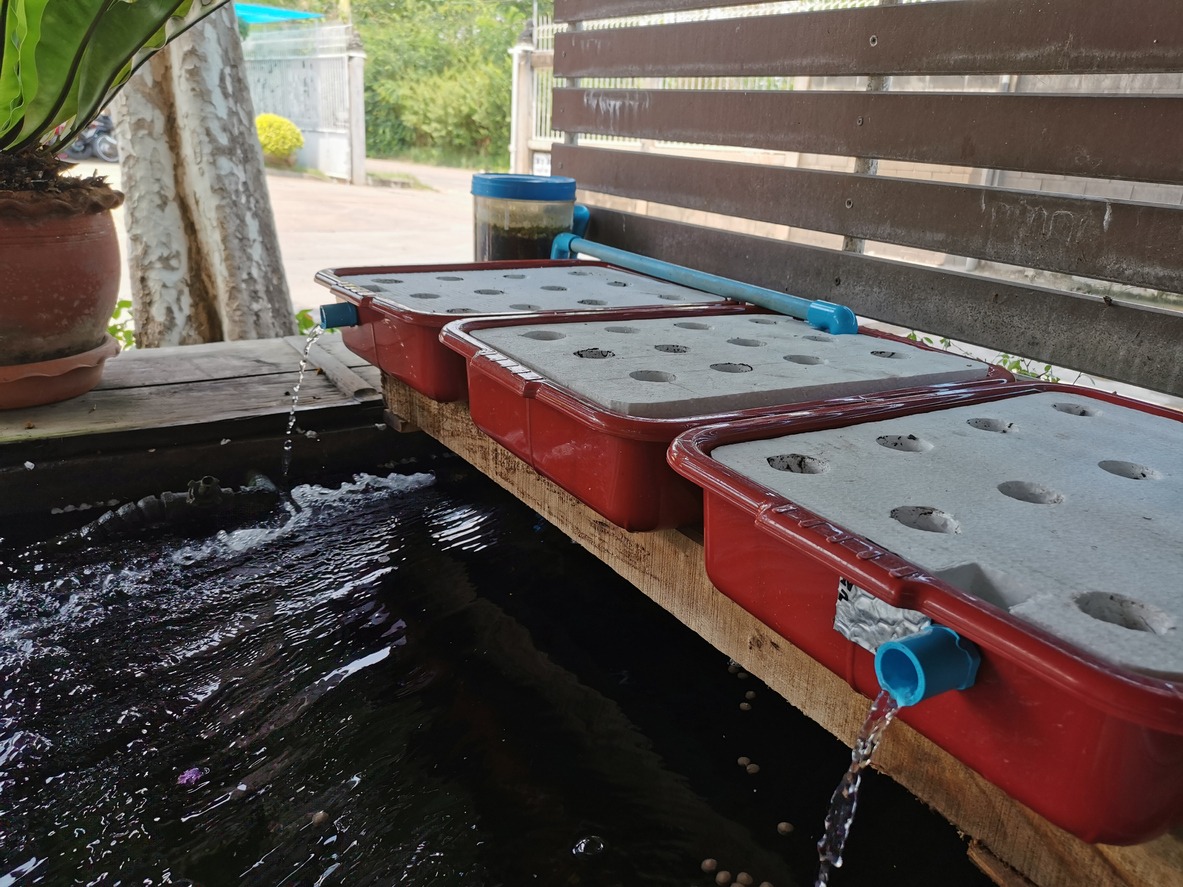
The grow bed, in which the plants are kept, is located directly above the fish tank. These beds can be filled with many different types of growing media, ranging from gravel to clay pellets and everything in between. The plant roots grow deeper and deeper into this medium, which provides them with a steady supply of water that is rich in nutrients.
Pumps and Plumbing
In an aquaponic system, the pumping system is the circulatory system. They are responsible for transporting water from the fish tank to the grow bed and then back again. This continuous flow not only aerates and oxygenates the water for the fish but also guarantees that the plants will have a steady supply of nutrients.
Beneficial Bacteria
These minuscule organisms are extremely important to the functioning of the system. They start with ammonia, which is found in fish waste, and convert it into nitrites and then nitrates. The nutrient cycle is considered to be complete when these nitrates are used by the plants as their primary source of nutrients.
Aquaponics vs. Traditional Farming
Water Efficiency
The use of water in conventional farming is a resource that must be carefully managed because it is frequently in short supply. On the other hand, aquaponics makes significantly better use of the water that is available. Because it is a closed-loop system, water is continuously recycled, and the amount of water lost to evaporation and runoff is kept to a minimum.
Space Utilization
Large swaths of arable land are typically required for traditional farming methods. Because of its vertical growing systems and compact design, aquaponics is a great option for people who have limited space because it can be implemented in small urban spaces or even indoors. This makes it an ideal choice for people who want to grow their food but do not have much room.
Chemical Inputs
Conventional farming frequently makes use of artificial substances like fertilizers and pesticides. In aquaponics, the use of such chemical inputs is minimized thanks to the natural processes that are already taking place. This not only has positive effects on the environment but also results in produce that is free of any harmful chemicals.
Setting Up Your Aquaponics System
To get started with aquaponics, you will need to do some careful planning, pick your fish and plants with consideration, and gather all of the necessary equipment. Let’s take a look at the primary actions that need to be taken to establish a productive and long-term aquaponics system.
Planning and Design
Location Considerations
The success of your aquaponic system is highly dependent on your ability to select the ideal location. Careful consideration should be given to several factors, including proximity to a water source, exposure to sunlight, and protection from adverse weather conditions.
System Size and Scale
Determine the size and scale of your system based on the amount of space you have available, the amount of yield you intend to achieve, and your preferences. Larger outdoor systems can support more extensive farming endeavors, while more compact indoor systems can provide fresh produce for personal use.
System Layout
Create a drawing of the layout, which should include the positioning of the grow bed(s), fish tank, pumps, and plumbing. It is important to think about things like gravity flow, ease of access for maintenance, and making the most of available space.
Choosing the Right Fish and Plants
Fish Selection
Choose fish species that are a good fit for the conditions of your climate and the regulations in your area. Popular options include tilapia, trout, and catfish; however, each of these fish has specific requirements concerning the temperature and pH levels of the water in which they are kept.
Plant Selection
Pick vegetation that does well in water-based systems like aquaponics. Because of their superior capacity to take in nutrients, foods such as lettuce, kale, and herbs are consistently among the most popular selections. However, plants that bear fruit, such as tomatoes and peppers, can also be grown successfully in larger systems.
The Aquaculture Component
The aquaculture part of the aquaponics system is the one that gets things going for the whole thing. It entails the raising of fish, which results in the establishment of a relationship between the growth of plants and that of aquatic life that is mutually beneficial. Let’s delve deeper into the fundamental components of effectively managing this essential component.
Types of Fish Suitable for Aquaponics
Tilapia
Because of its versatility and fast growth rate, tilapia is a fish that is frequently used in aquaponics systems. They can adapt to a wide range of climatic and aquatic conditions, and they do best in warm environments. In addition, tilapia are prized for the mild flavor and high nutritional value of their flesh, which makes them a popular option for the production of protein in a sustainable manner.
Catfish
Aquaponic systems would also benefit greatly from the addition of catfish to the fish population. They are resilient, able to adjust to new conditions, and are a good fit for a diverse range of environments. Catfish offer a dependable source of protein and, with the appropriate level of care and attention, have the potential to flourish as an integral part of your aquaponic ecosystem.
Trout
Trouts are a favorite among aquaponics enthusiasts in regions with cooler climates because they thrive in the conditions that trout prefer. They require temperatures in the water that are slightly lower than those required by other species, making them an ideal choice for systems in which it is easier to keep the water at a cooler temperature.
Fish Health and Maintenance
Monitoring Water Parameters
It is critical to the health of your fish that you keep the water conditions at their ideal level. Perform routine tests for a variety of parameters, including temperature, pH level, ammonia, nitrites, and nitrates. To maintain a stable and healthy environment, adjustments need to be made as soon as possible.
Feeding Regimen
Give your fish a diet that is well-rounded and suitable for their needs. Pellets of commercial fish food are easily accessible and specifically formulated to satisfy the dietary requirements of fish. Keep an eye on their eating patterns to prevent overfeeding, which can cause problems with the water’s quality.
Disease Prevention and Treatment
It is important to be vigilant when observing fish behavior and health to detect any potential problems promptly. Before releasing newly acquired fish into the main system, they should first be placed in quarantine, and you should also devise a strategy for isolating and treating sick fish if it becomes necessary.
Water Quality Management
Filtration and Aeration
It is vital to have effective filtration systems to remove solid waste and preserve the clarity of the water. In addition, aeration devices ensure that fish receive the appropriate amount of oxygen, which is beneficial to their overall health.
Monitoring and Adjusting pH Levels
It is essential for the health of both fish and plants to keep the pH level stable. To guarantee that the conditions are always at their best for each component of the system, perform routine pH tests and make necessary adjustments as required.
Managing Nutrient Levels
It is essential for the growth of healthy plants to keep the levels of nutrients in the system in balance. Ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels should all be monitored regularly to prevent imbalances that could be harmful to fish as well as plants.
The Hydroponics Component
The hydroponics component of an aquaponics system is the part of the system in which plants are grown in an environment without soil. These plants get the essential nutrients they need from the waste produced by the fish. A thriving aquaponic system that can maintain its sustainability requires that this aspect be mastered. Let’s take a look at some of the fundamental components of hydroponics that are used in aquaponics.
Types of Plants Suitable for Aquaponics
Leafy Greens (Lettuce, Kale, Spinach)
Because they absorb nutrients so effectively and their life cycles are so short, leafy greens are ideally suited for cultivation in aquaponic systems. Because they do so well in the nutrient-dense water that is delivered by the aquaponic system, selecting them as a crop to grow in such a system is a wise decision.
Herbs (Basil, Mint, Cilantro)
Aquaponics is an ideal system for growing herbs, which not only add flavor but also fragrance to the food you grow. Because of their generally small size and shallow root systems, they are an excellent candidate for cultivation in the majority of aquaponic systems.
Fruiting Plants (Tomatoes, Peppers)
Fruiting plants can flourish in aquaponic environments, even though they have higher nutrient requirements. They can successfully be grown in larger setups with sufficient levels of nutrients, and they provide a wider selection of produce to choose from.
Planting and Harvesting
Seeding or Transplanting
Depending on the kinds of plants you want to cultivate, you will either sow seeds or transplant seedlings into the grow bed you have prepared. For optimal growth, make sure the plants have adequate space between them and think about how big they will get.
Growth Monitoring
Always keep an eye on the development and well-being of the plant. Always be on the lookout for any symptoms that could indicate a lack of nutrients, pests, or diseases. If necessary, adjust the levels of the nutrients, and take corrective action as soon as possible.
Harvesting
Take cuttings from plants when they have reached their full maturity for the best flavor and most nutrients. To protect the plants from harm and to keep the growing environment in good condition, always use clean and sharp tools.
Nutrient Management
Nutrient Uptake
The nutrient-dense water that is supplied by an aquaponic system is essential for the growth of plants using hydroponics. The growth of your chosen plants must have a solid understanding of the specific nutrient requirements they have.
Monitoring pH Levels
It is important to keep the pH level within the range that is ideal for the plants you have chosen. By performing testing and making necessary adjustments regularly, one can ensure that nutrients are easily absorbable by the body.
Balancing Nutrient Levels
To prevent imbalances in the system that could affect plant growth, the nutrient levels should be monitored regularly. Make any necessary adjustments to preserve a thriving and fruitful hydroponic environment.
System Maintenance
It is essential to maintain your aquaponics system if you want it to continue to be successful and productive over the long term. With proper maintenance, their mutually beneficial environment will support the growth of both fish and plants. Let’s explore deeper into the fundamental components that make up effective aquaponics system maintenance.
Daily and Weekly Tasks
Feeding Fish
You should give your fish a well-rounded diet so that they receive all of the nutrients necessary for their development and continued good health. Keep an eye on their eating patterns to stop them from overeating, which can cause problems with the water’s quality.
Monitoring Water Parameters
Maintain a consistent monitoring and adjusting schedule for the water’s temperature, pH level, and nutrient levels. This daily task is necessary to keep the environment stable for the fish as well as the plants.
Visual Inspection
Conduct routine checks to determine whether the system exhibits any signs of damage, such as leaks or irregularities. The prompt identification of problems enables timely intervention and protects against the possibility of system breakdowns.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Algae Growth
The quality of the water may suffer if algae are allowed to proliferate within the system. To prevent the growth of an excessive amount of algae, employ light-blocking strategies such as using shade cloth or storing water in dark-colored tanks.
pH Fluctuations
It is essential to keep the pH level stable. To maintain conditions that are favorable for fish and plants, it is necessary to monitor the pH level of the water and, if necessary, use pH stabilizers or other natural buffering agents to bring it back into the ideal range.
Nutrient Imbalances
Always keep an eye on the nutrient levels in the soil and make any necessary adjustments to prevent nutrient deficiencies or excesses, both of which can stunt plant growth. Adjust the settings of the system so that it has a nutrient balance that is in perfect harmony.
Seasonal Considerations
Temperature Management
If you live in a more temperate climate, you might want to think about insulating the system or using a greenhouse to control the temperature. It is possible that shading and ventilation will be required to prevent overheating in warmer climates.
Adjusting Feeding Regimen
temperature changes may cause variations in the metabolic rate of fish. Adjust the feeding schedule and the amount of food given to the fish so that it meets its requirements throughout the year.
Plant Selection and Rotation
When selecting plants for your aquaponic system, you should take into consideration seasonal variations. Certain temperatures or light conditions may be optimal for the growth of certain crops, which paves the way for a more varied and flexible harvest.
Off-Grid Considerations
Off-grid aquaponics provides a one-of-a-kind answer for people who are interested in achieving self-sufficiency and long-term sustainability. It is a novel method of farming that coexists peacefully with the natural world and functions in a manner that is independent of conventional utilities. Let’s take a look at some of the most important things to think about when operating an aquaponics system off the grid.
Energy Requirements
Renewable Energy Sources
Off-grid aquaponics systems typically satisfy their energy requirements through the utilization of renewable energy sources like solar panels or wind turbines. These sources provide an energy supply that is both reliable and sustainable, thereby reducing the need for reliance on the grid.
Energy-Efficient Components
It is essential to choose energy-efficient equipment to cut down on energy consumption. Some examples of energy-efficient equipment include pumps with low wattage and lighting with LEDs. This not only lessens the impact on the environment but also helps to keep operational costs to a minimum.
Battery Storage Systems
Off-grid systems rely heavily on energy storage solutions such as battery banks to ensure a continuous power supply, particularly during times of low generation of renewable energy. These battery banks play a crucial role in off-grid systems.
Water Source and Management
Rainwater Collection
Rainwater collection is frequently utilized as the primary source of water in off-grid aquaponics systems. In times of drought, having reliable water collection and storage methods is necessary to make the most of the available water.
Water Filtration and Purification
Systems that are not connected to the grid ought to have efficient filtration and purification mechanisms built into them to guarantee adequate water quality for aquatic life and plant life alike. This may involve the use of sediment filters, ultraviolet (UV) sterilizers, or other methods of water treatment.
Water Recycling and Conservation
It is essential to put in place effective practices for water recycling if one wishes to reduce the amount of water that is wasted. Off-grid systems can function with a smaller impact on the surrounding environment if they recycle and replenish the water that is used within the system.
Scalability and Adaptability
Modular Design
Off-grid aquaponics systems need to be designed with expansion in mind to be successful. Components that can be easily expanded or adapted to accommodate shifting requirements or objectives are known as modular.
Climate Considerations
When designing an off-grid system, it is important to consider the local climate. To ensure year-round productivity, it is important to put into place strategies for regulating temperatures, providing insulation, and shielding against extreme weather events.
Integration with Other Systems
Living off the grid typically requires adopting a more holistic approach to the task of achieving self-sufficiency. Consider how the aquaponics system can be combined with other environmentally friendly methods, such as the collection of rainwater, the generation of renewable energy, or composting.
Conclusion
Learning the fundamentals of aquaponics opens up a world of off-grid, sustainable farming opportunities. This clever combination of hydroponics and aquaculture creates a thriving environment for plants and fish while also serving as a model for future environmentally friendly practices. One can take a step toward self-sufficiency, renewable energy generation, water conservation, and climate adaptation by learning about the science, parts, and upkeep of an aquaponic system.
Aquaponics offers hope for a more resilient, sustainable, and integrated farming method with careful planning and dedication to fostering this harmonious cycle. Adhering to these values not only keeps us alive but also takes care of the earth we live on.