As of August 29, 2016, the Federal Aviation Administration published new rules for unmanned aerial systems (UAS) under Part 107.
The rules not only included operation rules for small UAS, but it also created the Remote Pilot Certificate with a Small UAS Rating, the first and only airman certificate specifically for the use and operation of small UAS.
In order to use a small UAS or drone commercially in the United States, pilots are required to obtain their Remote Pilot Certificate.
Once a pilot has their Remote Pilot Certificate they are able to operate registered small UAS weighing less than 55 pounds for commercial purposes. The UAS has to be kept within visual line-of-sight, it must be used during the day, and cannot go higher than 400 feet above ground level.
UAS cannot be flown above 100 miles per hour, over people, in restricted areas, or from a moving vehicle, unless specific waivers are obtained. It is also required that all UAS yield to manned aircraft at all times.
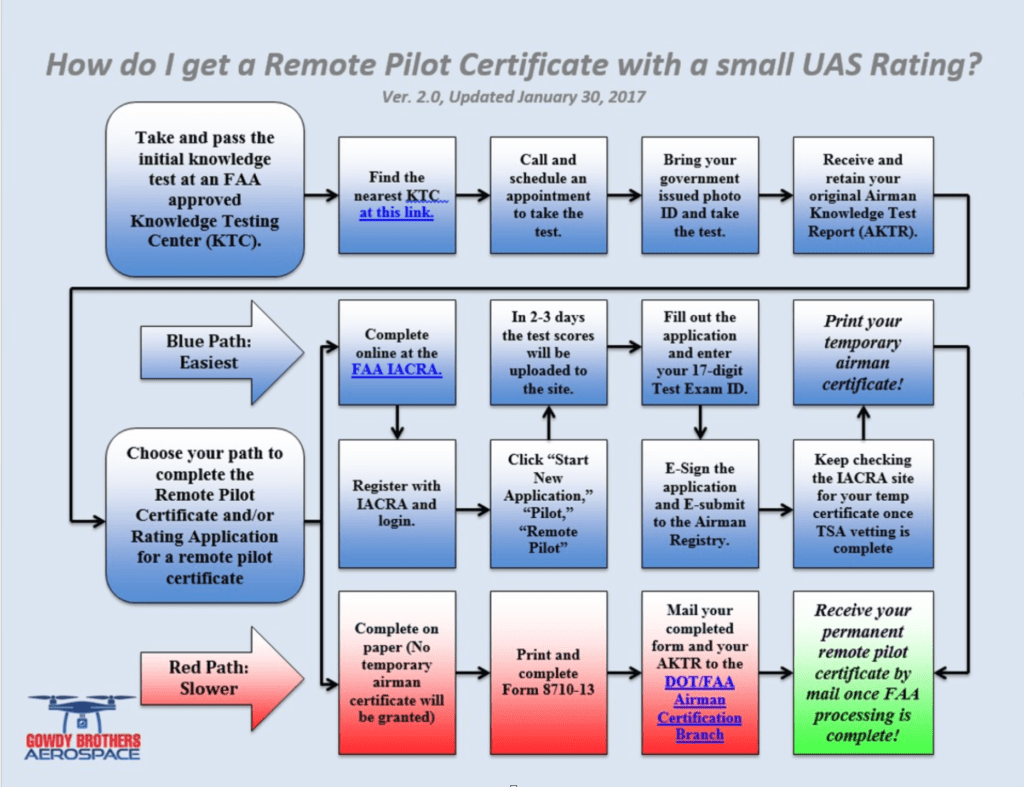
There are two different paths to obtaining your Remote Pilot Certificate depending on whether you are a pilot or not.
For Existing Part 61 Pilots
To qualify for a remote pilot certificate, a certified Pilot must:
1. Hold a part 61 pilot certificate other than student pilot
2. Complete a small UAS online training course provided by the FAA
3. Complete a flight review within the previous 24 months
4. Be at least 16 years old
Part 61 pilot certificate holders may obtain a temporary remote pilot certificate immediately upon submission of their application for a permanent certificate
For All Others
To qualify for a remote pilot certificate, a person must:
1. Demonstrate aeronautical knowledge
2. Pass an initial Aeronautical Knowledge Test at an FAA-approved knowledge testing center
3. Complete a flight review within the previous 24 months
4. Be vetted by the Transportation Security Administration
5. Be at least 16 years old
Applicants will obtain a temporary remote pilot certificate upon successful completion of TSA security vetting
Test areas covered by the Aeronautical Knowledge Test include:
1. Applicable regulations relating to small unmanned aircraft system rating privileges, limitations, and flight operation
2. Airspace classification and operating requirements, and flight restrictions affecting small unmanned aircraft operation
3. Aviation weather sources and effects of weather on small unmanned aircraft performance
4. Small unmanned aircraft loading and performance
5. Emergency procedures
6. Crew resource management
7. Radio communication procedures
8. Determining the performance of small unmanned aircraft
9. Physiological effects of drugs and alcohol
10. Aeronautical decision-making and judgment
11. Airport operations
12. Maintenance and preflight inspection procedures
It takes 48 hours for the FAA to get access to your test scores, so once you pass your Aeronautical Knowledge Test, wait two days and then create an account on the FAA’s IACRA website.
Once you’re logged in, follow the instructions to apply for your Remote Pilot Certificate. After you send in your application, you’ll go through automatic TSA security vetting, and once you are cleared, they will send you a temporary electronic Remote Pilot Certificate.
A permanent remote pilot certificate will be sent via mail once all other FAA-internal processing is complete.